unRAID
DO NOT use the template paths from unRAID or the suggested paths from SpaceInvader One.
SpaceInvader One YouTube guides are great for learning how to start with unRAID or how to set up certain applications - and yes I did and still do use them.
The main reason why he's probably using those paths is because they are predefined in the templates.
Preparation
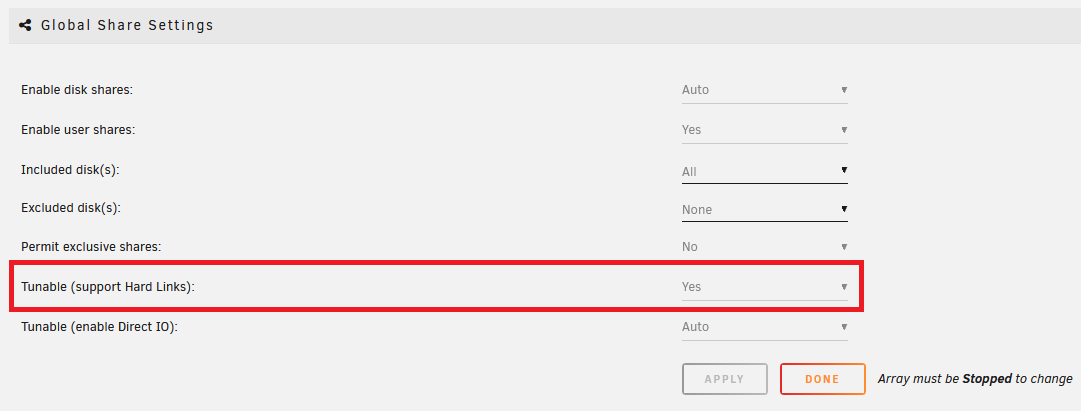
Make sure Tunable (support Hard Links) is enabled in your Settings => Global Share Settings.
Create the main share
To get Hardlinks and Atomic-Moves working with unRAID,
You will need to make use of ONE share with subfolders.
In this example, I'm using my own setup and the preferred share data.
Go to your dashboard and select Shares on the navigation bar, then choose Add Share.
- Use
data -
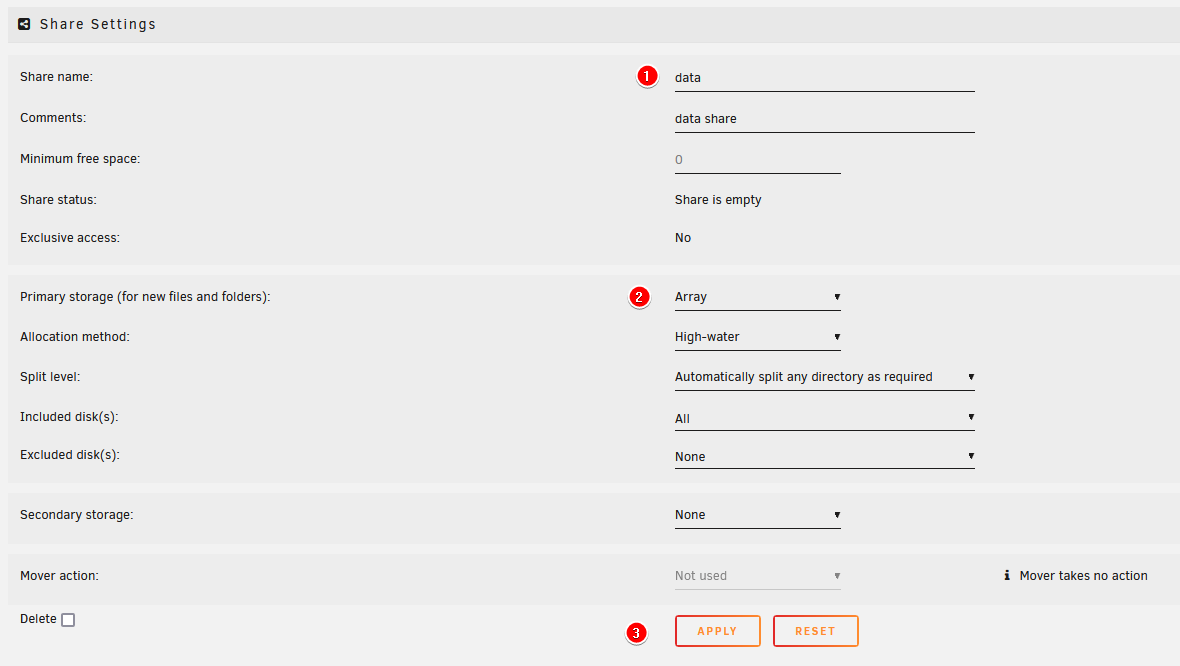
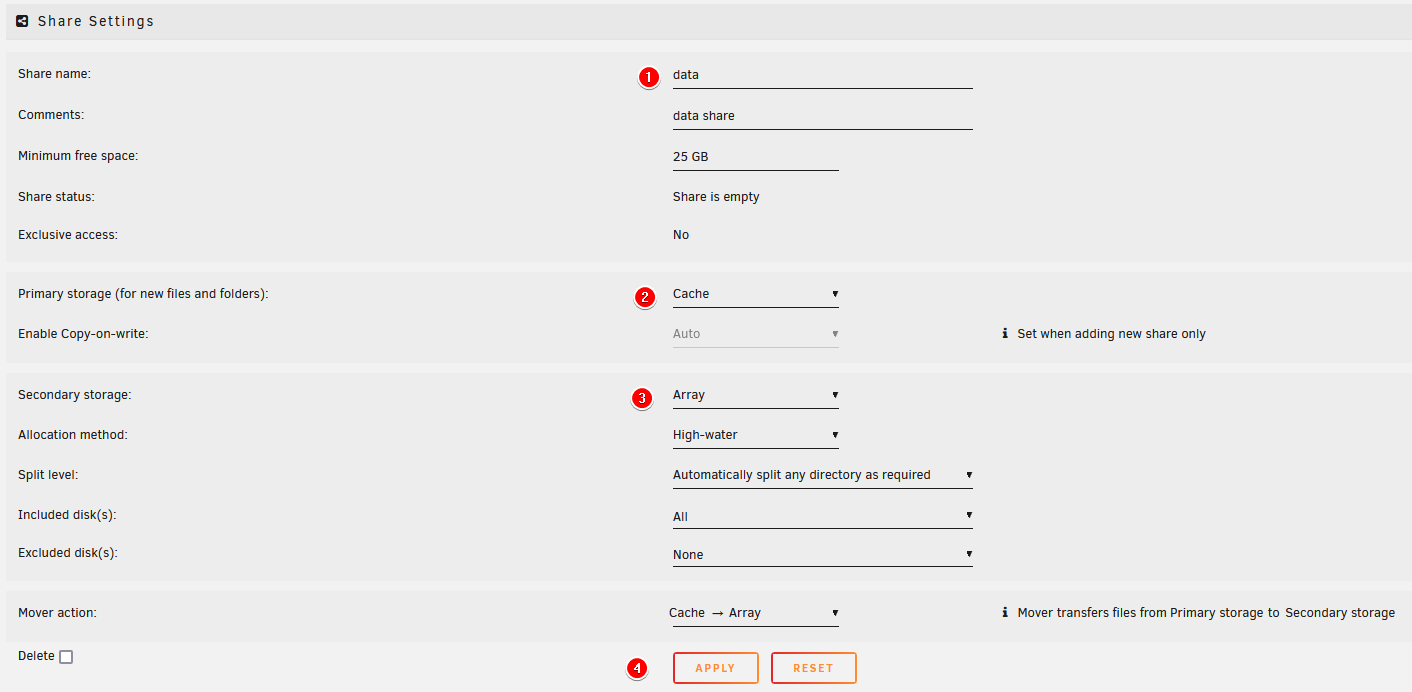
Set up your share with the applicable settings.
Select the
Primary storageasArray(shown in theNo Cachetab above).- Select the
Primary storageasCache(shown in theCachetab above). - Select the
Secondary storageasArray - Make sure
Mover actionis set toCache -> Array
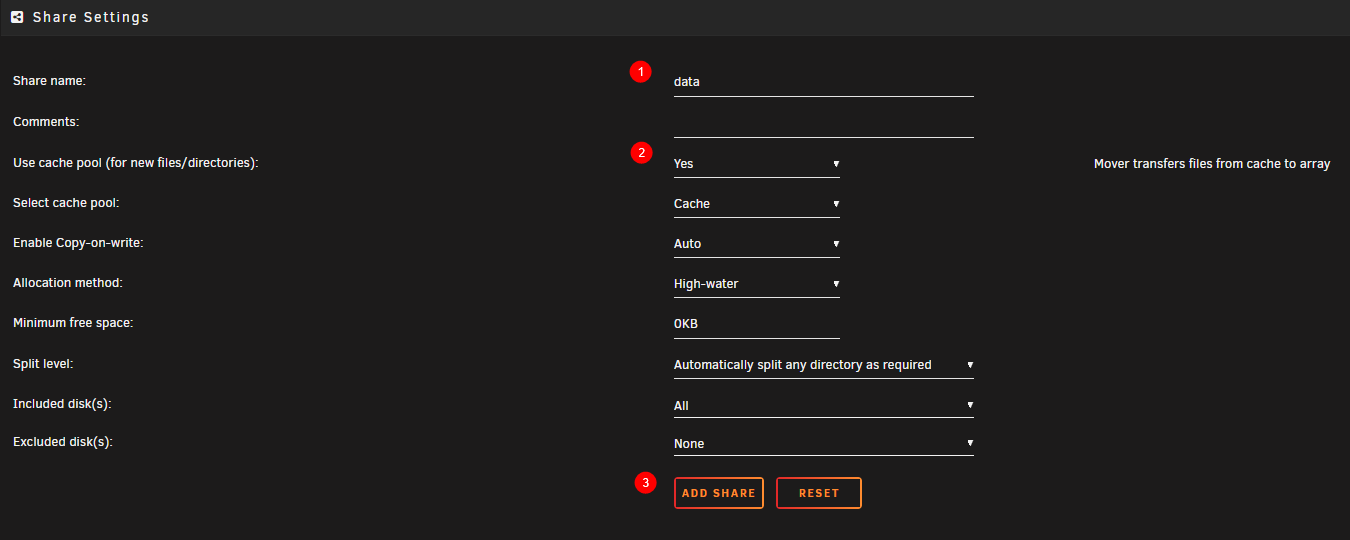
Choose
Yeson step (2) (unRAID 6.11 tab above). If not using a cache drive, keep this option disabled.Hardlinks will stay intact if you're using a cache
- Select the
-
Click on
ADD SHARE
Note
Keep in mind, regarding the use of the cache drive, unRAID's integrated mover cannot move files that are in use, like seeding torrents. You will need to stop/pause the torrents so the mover can move the files from the cache to your array.
If you use qBittorrent you can automate the process by following the following Guide HERE
If you use Deluge you can automate the process by following the following Guide HERE
With Usenet, you won't have any issues.
Folder Structure
On the host (unRAID) you will need to add /mnt/user before it. So /mnt/user/data
The data folder has sub-folders for torrents and usenet, and each of these has sub-folders for tv, movie and music downloads to keep things organized. The media folder has nicely named TV, Movies and Music sub-folders, this is where your library resides, and what you’d pass to Plex, Emby or JellyFin.
You will need to create these subfolders yourself. You can do this any way you prefer, but Krusader or WinSCP are popular choices if you are unsure.
data
├── torrents
│ ├── books
│ ├── movies
│ ├── music
│ └── tv
├── usenet
│ ├── incomplete
│ └── complete
│ ├── books
│ ├── movies
│ ├── music
│ └── tv
└── media
├── books
├── movies
├── music
└── tv
I'm using lower-case on all folders on purpose, being Linux is case-sensitive.
Breakdown of the Folder Structure
Bad path suggestion
The default path setup suggested by some docker developers that encourages people to use mounts like /movies, /tv, /books or /downloads is very suboptimal and it makes them look like two or three file systems, even if they aren’t (Because of how Docker’s volumes work). It is the easiest way to get started. While easy to use, it has a major drawback. Mainly losing the ability to hardlink or instant move, resulting in a slower and more I/O intensive copy + delete is used.
Setting up the containers
After you've created all the necessary folders, it's time to set up the Docker container's paths.
Go to your dashboard and select the Docker container you want to edit, or, if you're starting fresh, add the container/App you want to use.
unRAID makes it pretty clear which is the Host Path and Container Path.
Container Path: => The path that will be used from inside the container.
Host Path: => The actual/absolute path used on your unRAID Server (The Host).
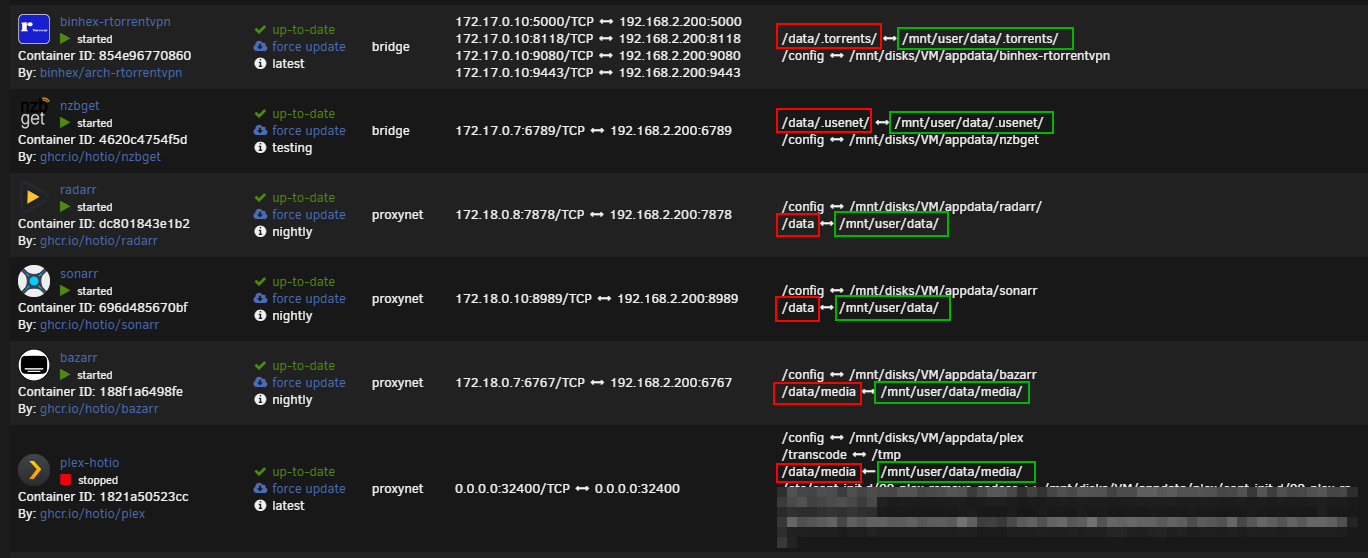
Torrent clients
qBittorrent, Deluge, ruTorrent
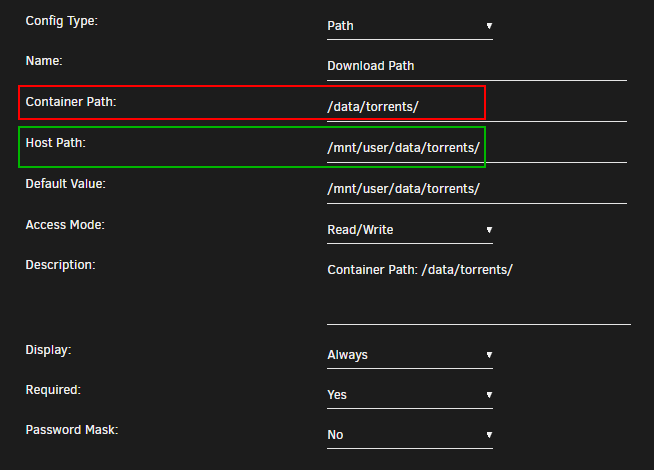
Container Path: => /data/torrents/
Host Path: => /mnt/user/data/torrents/
Info
The reason why we use /data/torrents/ for the torrent client is because it only needs access to the torrent data. In the torrent software settings, you’ll need to configure your categories/labels to utilize the right path for specific content. You can sort into sub-folders like /data/torrents/{tv|movies|music}.
data
└── torrents
├── books
├── movies
├── music
└── tv
Usenet clients
NZBGet or SABnzbd
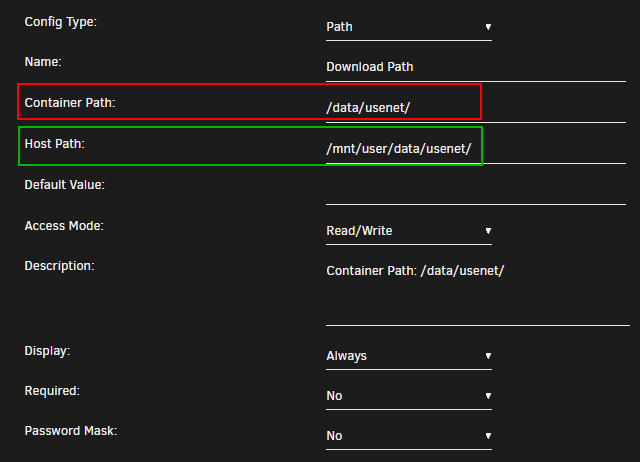
Container Path: => /data/usenet/
Host Path: => /mnt/user/data/usenet/
Info
The reason why we use /data/usenet/ for the usenet client is that it only needs access to the usenet data. In the usenet software settings, you’ll need to configure your paths to sort content into sub-folders like /data/usenet/{tv|movies|music}.
data
└── usenet
├── incomplete
└── complete
├── books
├── movies
├── music
└── tv
The Starr Apps
Sonarr, Radarr and Lidarr
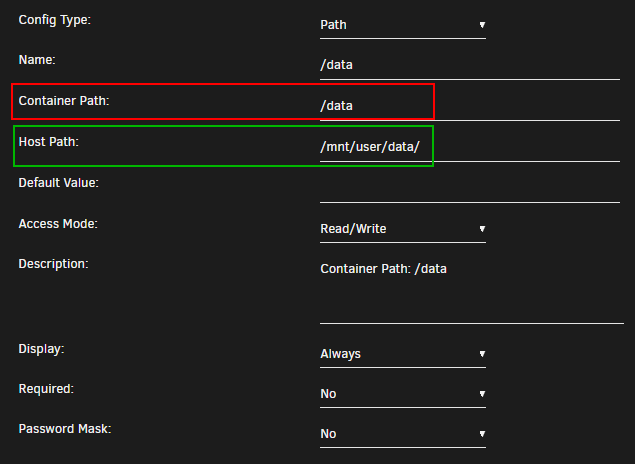
Container Path: => /data
Host Path: => /mnt/user/data/
Info
Sonarr, Radarr and Lidarr get access to everything because the download folder(s) and media folder will need to look like, and be one mount, on the file system. Hard links will work properly and any moves will be atomic, rather than copying and deleting.
data
├── torrents
│ ├── books
│ ├── movies
│ ├── music
│ └── tv
├── usenet
│ ├── incomplete
│ └── complete
│ ├── books
│ ├── movies
│ ├── music
│ └── tv
└── media
├── books
├── movies
├── music
└── tv
Media Server
Plex, Emby, JellyFin and Bazarr
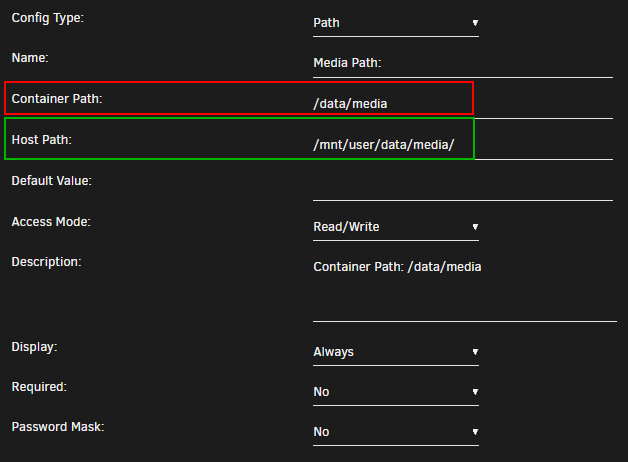
Container Path: => /data/media
Host Path: => /mnt/user/data/media/
Info
Plex, Emby, JellyFin and Bazarr only need access to your media library, which can have any number of sub-folders (Movies, Kids Movies, TV, Documentary TV and/or Music).
data
└── media
├── movies
├── music
├── books
└── tv
Final Result
Don't forget to look at the Examples of how to set up your paths INSIDE your applications.
Video Tutorial
Big Thanks to IBRACORP for noticing this Guide and creating a Video covering this unRAID section.
The reason why I have this video at the end is because I want the users to ACTUALLY LEARN and UNDERSTAND why it's recommended to use this folder structure prior to going straight to a YouTube video.
Check out other videos from IBRACORP HERE