|
|
2 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .github | 2 years ago | |
| ass-x@2b143138ef | ||
| gfycat | ||
| install | ||
| src | 2 years ago | |
| views | ||
| .deepsource.toml | ||
| .gitignore | 2 years ago | |
| .gitmodules | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| MagicNumbers.json | ||
| compose.yaml | ||
| flameshot_example.sh | ||
| package-lock.json | 2 years ago | |
| package.json | 2 years ago | |
| sample_config.sxcu | ||
| tailwind.config.js | ||
| tailwind.css | ||
| tsconfig.json | 2 years ago | |
.github/README.md
ass is a self-hosted ShareX upload server written in Node.js. I initially started this project purely out of spite. ass aims to be as unopinionated as possible, giving users & hosts alike the ability to modify nearly everything.
By default, ass comes with a resource viewing page, which includes metadata about the resource as well as a download button & inline viewers for images, videos, & audio. It does not have a user dashboard or registration system: this is intentional! Developers are free to create their own frontends using the languages & tools they are most comfortable with. Writing & using these frontends is fully documented below, in the wiki, & in the source code.
Developers ❤
ass was designed with developers in mind. If you are a developer & want something changed to better suit you, let me know & we'll see what we can do!
Code quality
| CodeQL | DeepSource |
|---|---|
Features
For users
- Upload images, gifs, videos, audio, & files
- Token-based authentication
- Download & delete resources
- GPS data automatically removed
- Fully customizable Discord embeds
- Built-in web viewer with video & audio player
- Embed images, gifs, & videos directly in Discord
- Personal upload log using customizable Discord Webhooks
- macOS/Linux support with alternative clients such as Flameshot (script for ass) & MagicCap
- Multiple URL styles
- ZWS
- Mixed-case alphanumeric
- Gfycat
- Original
- Timestamp
For hosts & developers
- Usage metrics
- Thumbnail support
- Mimetype blocking
- Themeable viewer page
- Basic multi-user support
- Configurable global upload size limit (per-user coming soon)
- Custom pluggable frontends using Git Submodules
- Run locally or in a Docker container
- Multiple file storage methods
- Local file system
- Amazon S3, including DigitalOcean Spaces
- Skynet (free decentralized storage on the Sia blockchain)
- Multiple data storage methods using data engines
- File
- JSON (default, papito)
- YAML (soon)
- Database
- PostgreSQL (ass-psql)
- MongoDB (ass-mongoose)
- MySQL (soon)
- File
Access types
| Type | What is it? |
|---|---|
| Zero-width spaces | When pasted elsewhere, the URL appears to be just your domain name. Some browsers or sites may not recognize these URLs (Discord does support these) |
| Mixed-case alphanumeric | The "safe" mode. URL's are browser safe as the character set is just letters & numbers. |
| Gfycat | Gfycat-style ID's (for example: https://example.com/unsung-discrete-grub). Thanks to Gfycat for the wordlists |
| Original | The "basic" mode. URL matches the same filename as when the file was uploaded. This may be prone to conflicts with files of the same name. |
| Timestamp | The quick but dirty mode. URL is a timestamp of when the file was uploaded, in milliseconds. This is the most unique mode, but also potentially the longest (Gfycat could be longer, easily). Keep in mind this is vulnerable to iteration attacks |
Installation
ass supports two installation methods: Docker (recommended) & local (manual).
Docker
Expand for Docker/Docker Compose installation steps
Docker Compose is the recommended way to install ass. These steps assume you are already family with Docker. If not, you should probably use the local installation method. They also assume that you have a working Docker installation with Docker Compose v2 installed.
Install using docker-compose
- Clone the ass repo using
git clone https://github.com/tycrek/ass.git && cd ass/ - Run the command that corresponds to your OS:
- Linux:
./install/docker-linux.sh(uses#!/bin/bash) - Windows:
install/docker-windows.bat(from Command Prompt) - These scripts are identical using the equivalent commands in each OS.
- Linux:
- Work through the setup process when prompted.
The upload token will be printed at the end of the setup script prompts. This is the token that you'll need to use to upload resources to ass. It may go by too quickly to copy it, so just scroll back up in your terminal after setup or run cat auth.json.
You should now be able to access the ass server at http://localhost:40115/ (ass-docker will bind to host 0.0.0.0 to allow external access). You can configure a reverse proxy (for example, Caddy; also check out my tutorial) to make it accessible from the internet with automatic SSL.
What is this script doing?
It creates directories & files required for Docker Compose to properly set up volumes. After that, it simply builds the image & container, then launches the setup process.
How do I run the npm scripts?
Since all 3 primary data files are bound to the container with Volumes, you can run the scripts in two ways: docker compose exec or npm on the host.
# Check the usage metrics
docker compose exec ass npm run metrics
# Run the setup script
docker compose exec ass npm run setup && docker compose restart
# Run npm on the host to run the setup script (also works for metrics)
# (You will have to meet the Node.js & npm requirements on your host for this to work properly)
npm run setup && docker compose restart
How do I update?
Easy! Just pull the changes & run this one-liner:
# Pull the latest version of ass & rebuild the image
git pull && docker compose build --no-cache && docker compose up -d
What else should I be aware of?
Deploying ass with Docker exposes five volumes. These volumes let you edit the config, view the auth or data files, or view the uploads/ folder from your host.
uploads/share/config.jsonauth.jsondata.json
Local
Expand for local installation steps
- You should have Node.js 16 & npm 8 or later installed.
- Clone this repo using
git clone https://github.com/tycrek/ass.git && cd ass/ - Run
npm i --save-devto install the required dependencies (--save-devis required for compilation) - Run
npm run buildto compile the TypeScript files - Run
npm startto start ass.
The first time you run ass, the setup process will automatically be called & you will be shown your first authorization token; save this as you will need it to configure ShareX.
Using HTTPS
For HTTPS support, you must configure a reverse proxy. I recommend Caddy but any reverse proxy should work (such as Apache or Nginx). I also have a tutorial on easily setting up Caddy as a reverse proxy server.
Generating new tokens
If you need to generate a new token at any time, run npm run new-token <username>. This will automatically load the new token so there is no need to restart ass. Username field is optional; if left blank, a random username will be created.
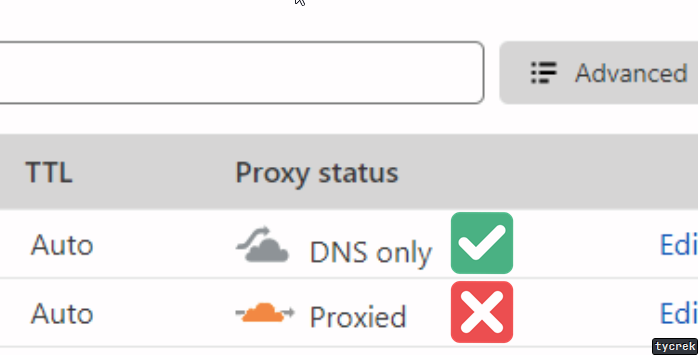
Cloudflare users
In your Cloudflare DNS dashboard, set your domain/subdomain to DNS Only if you experience issues with Proxied.
Configure ShareX
- Add a new Custom Uploader in ShareX by going to
Destinations > Custom uploader settings... - Under Uploaders, click New & name it whatever you like.
- Set Destination type to
Image,Text, &File - Request tab:
- Method:
POST - URL:
https://your.domain.name.here/ - Body:
Form data (multipart/form-data) - File from name:
file(literally put "file" in the field) - Headers:
- Name:
Authorization - Value: (the value provided by
npm starton first run)
- Name:
- Method:
- Response tab:
- URL:
{json:.resource} - Thumbnail:
{json:.thumbnail} - Deletion URL:
{json:.delete} - Error message:
{response} - MagicCap users: do not include the
.in the above & replace{}with$(i.e.$json:resource$)
- URL:
- The file
sample_config.sxcucan also be modified & imported to suit your needs
Header overrides
If you need to override a specific part of the config to be different from the global config, you may do so via "X" HTTP headers:
| Header | Purpose |
|---|---|
X-Ass-Domain |
Override the domain returned for the clipboard (useful for multi-domain hosts) |
X-Ass-Access |
Override the generator used for the resource URL. Must be one of: original, zws, gfycat, random, or timestamp (see above) |
X-Ass-Gfycat |
Override the length of Gfycat ID's. Defaults to 2 |
X-Ass-Timeoffset |
Override the timestamp offset. Defaults to UTC+0 |
Fancy embeds
If you primarily share media on Discord, you can add these additional (optional) headers to build embeds:
| Header | Purpose |
|---|---|
X-Ass-OG-Title |
Large text shown above your media |
X-Ass-OG-Description |
Small text shown below the title but above the media (does not show up on videos) |
X-Ass-OG-Author |
Small text shown above the title |
X-Ass-OG-Author-Url |
URL to open when the Author is clicked |
X-Ass-OG-Provider |
Smaller text shown above the author |
X-Ass-OG-Provider-Url |
URL to open when the Provider is clicked |
X-Ass-OG-Color |
Colour shown on the left side of the embed. Must be one of &random, &vibrant, or a hex colour value (for example: #fe3c29). Random is a randomly generated hex value & Vibrant is sourced from the image itself |
Embed placeholders
You can insert certain metadata into your embeds with these placeholders:
| Placeholder | Result |
|---|---|
&size |
The files size with proper notation rounded to two decimals (example: 7.06 KB) |
&filename |
The original filename of the uploaded file |
×tamp |
The timestamp of when the file was uploaded (example: Oct 14, 1983, 1:30 PM) |
Webhooks
You may use Discord webhooks as an easy way to keep track of your uploads. The first step is to create a new Webhook. You only need to follow the first section, Making a Webhook. Once you are done that, click Copy Webhook URL. Finally, add these headers to your custom uploader:
| Header | Purpose |
|---|---|
X-Ass-Webhook-Url |
The Webhook URL you copied |
X-Ass-Webhook-Username |
(Optional) the "username" of the Webhook; can be set to whatever you want |
X-Ass-Webhook-Avatar |
(Optional) URL to an image to use as the Webhook avatar. Use the full URL including https:// |
Webhooks will show the filename, mimetype, size, upload timestamp, thumbail, & a link to delete the file. To disable webhooks, simply remove the headers from your config.
Customizing the viewer
If you want to customize the font or colours of the viewer page, create a file in the share/ directory called theme.json. Available options are:
| Option | Purpose |
|---|---|
font |
The font family to use; defaults to "Josefin Sans". Fonts with a space should be surrounded by double quotes. |
bgPage |
Background colour for the whole page |
bgViewer |
Background colour for the viewer element |
txtPrimary |
Primary text colour; this should be your main brand colour. |
txtSecondary |
Secondary text colour; this is used for the file details. |
linkHover |
Colour of the hover effect for links |
linkActive |
Colour of the active effect for links |
borderHover |
Colour of the hover effect for borders; this is used for the underlining links. |
Custom index
By default, ass directs the index route / to this README. Follow these steps to use a custom index:
- Create a file in the
share/directory calledindex.htmlorindex.js.- ass will treat
index.htmlas an HTML file and will send it to the client. - ass will treat
index.jsas a Node.js file that exports a function representing Express middleware. ass will pass all handling of the index to this function. The function should take three arguments:(req, res, next). Some code samples for common use cases are provided below. - If both
index.htmlandindex.jsare present, theindex.htmlfile will be served first.
- ass will treat
- Add whatever you want to the file.
- Restart ass. The startup info logs should mention which file is being used as the index.
Custom index code samples
Redirect to a custom frontend registration page
module.exports = (req, res, next) => res.redirect('/register');
File storage
ass supports three methods of file storage: local, S3, or Skynet.
Local
Local storage is the simplest option, but relies on you having a lot of disk space to store files, which can be costly.
S3
Any existing object storage server that's compatible with Amazon S3 can be used with ass. I personally host my files using Digital Ocean Spaces, which implements S3.
S3 servers are generally very fast & have very good uptime, though this will depend on the hosting provider & plan you choose.
Skynet
As of August 12, 2022, Skynet Labs is shut down. Skynet will continue to work, as such is the nature of decentralized services.
Skynet is a decentralized CDN created by Skynet Labs. It utilizes the Sia blockchain, the leading decentralized cloud storage platform, which boasts "no signups, no servers, no trusted third parties". For hosts who are looking for a reliable, always available storage solution with lots of capacity & no costs, Skynet may be your best option. However, uploads tend to be on the slower side (though speeds will improve as the Sia network grows).
Custom frontends - OUTDATED
Please be aware that this section is outdated (marked as of 2022-04-15). It will be updated when I overhaul the frontend system.
ass is intended to provide a strong backend for developers to build their own frontends around. Git Submodules make it easy to create custom frontends. Submodules are their own projects, which means you are free to build the router however you wish, as long as it exports the required items. A custom frontend is really just an Express.js router.
For a detailed walkthrough on developing your first frontend, consult the wiki.
Data Engines
Papito data engines are responsible for managing your data. "Data" has two parts: an identifier & the actual data itself. With ass, the data is a JSON object representing the uploaded resource. The identifier is the unique ID in the URL returned to the user on upload. Update August 2022: I plan to overhaul Papito and how all this works eventually. If this comment is still here in a year, kick message me.
Supported data engines:
| Name | Description | Links |
|---|---|---|
| JSON | JSON-based data storage. On disk, data is stored in a JSON file. In memory, data is stored in a Map. This is the default engine. | GitHub npm |
| PostgreSQL | Data storage using a PostgreSQL database. node-postgres is used for communicating with the database. | GitHub npm |
| Mongoose | Data storage using a MongoDB database. mongoose is used for communicating with the database. Created by @dylancl | GitHub npm |
A Papito data engine implements support for one type of database (or file, such as JSON or YAML). This lets ass server hosts pick their database of choice, because all they'll have to do is enter the connection/authentication details & ass will handle the rest, using the resource ID as the key.
For a detailed walkthrough on developing engines, consult the wiki. Outdated!
npm scripts
ass has a number of pre-made npm scripts for you to use. All of these scripts should be run using npm run <script-name> (except start).
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
start |
Starts the ass server. This is the default script & is run with npm start. |
build |
Compiles the TypeScript files into JavaScript. |
dev |
Chains the build & compile scripts together. |
setup |
Starts the easy setup process. Should be run after any updates that introduce new config options. |
metrics |
Runs the metrics script. This is a simple script that outputs basic resource statistics. |
purge |
Purges all uploads & data associated with them. This does not delete any users, however. |
new-token |
Generates a new API token. Accepts one parameter for specifying a username, like npm run new-token <username>. ass automatically detects the new token & reloads it, so there's no need to restart the server. |
engine-check |
Ensures your environment meets the minimum Node & npm version requirements. |
Flameshot users (Linux)
Use this script. For the KEY, put your token. Thanks to @ToxicAven for creating this!
Contributing
Please follow the Contributing Guidelines when submiting Issues or Pull Requests.