15 KiB
Synology
!!! note
Being I don't have a Synology myself and I kind of hate the Synology GUI for the dockers, we're going to do this with the use of docker-compose through a terminal.
This is faster than the GUI and after installing, it shows up in the Docker GUI.
Thanks to faxity for the initial compose that I used to create the Synology Guide.
And a very big thanks to [Bokkoman](https://www.buymeacoffee.com/bokkoman){:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"} and [BZwart](https://github.com/BaukeZwart){:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"} that updated this Guide for DSM 7 and also offered their help on discord as Synology Support Team.
Introduction
This page will provide you with guidance on how to install several Docker images related to the Servarr apps to your Synology. We highly recommend reading the full guide, that way you have a better understanding of what you do, in case you later decide to make changes.
Summary
- We will create one share that will hold all your data. This ensures hardlinking and/or instant moves are possible.
- Create one user that will be assigned to the docker images as the user they run out of security reasons.
- Create a folder structure on the
dataanddockershare with a few commands (or manually). - Download and edit the
docker-compose.ymland.envfiles to your system settings. - Set permissions to all folders related to the shares.
- Run and execute docker commands to start the containers.
Automated Script
??? example "Automated script (‼️Use this script at your own risk‼️) - [Click to show/hide]"
!!! Warning
Though, we offer a short way out. This is intended as a quick way to do everything that is written on this page within one script. And is only for initial setup. After that, you need to manage it yourself. Rerunning the script can or will reset all personal changes made in the compose/env.
The script is only tested on Synology DSM7 and higher.
**:bangbang: We are not held liable if anything breaks on your system. Use at your own risk :bangbang:**
To get this working you will need to enable terminal access (SSH) and home folders.
Be sure to delete current running Docker containers related to this guide (ie. *arr apps, download clients), and backup settings before you do.
To enable SSH on your Synology take a look [HERE](#ssh){:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"}.
To enable Home folders, go to `Control Panel` > `User & Group` > `Advanced` > `Enable user home service` at the bottom.

When you enable these two settings, run the following commands in your favorite terminal app and follow the onscreen questions.
```bash
curl -sL git.io/syno-script > ~/syno-script
```
```bash
sudo bash ~/syno-script
```
Install Docker
You need to install Docker / Container Manager from the Package Center. This should also create a share named docker, and check File Station if it is present.
Create the main share
We will create and use a new share named data (lowercase) for all your library media and downloads.
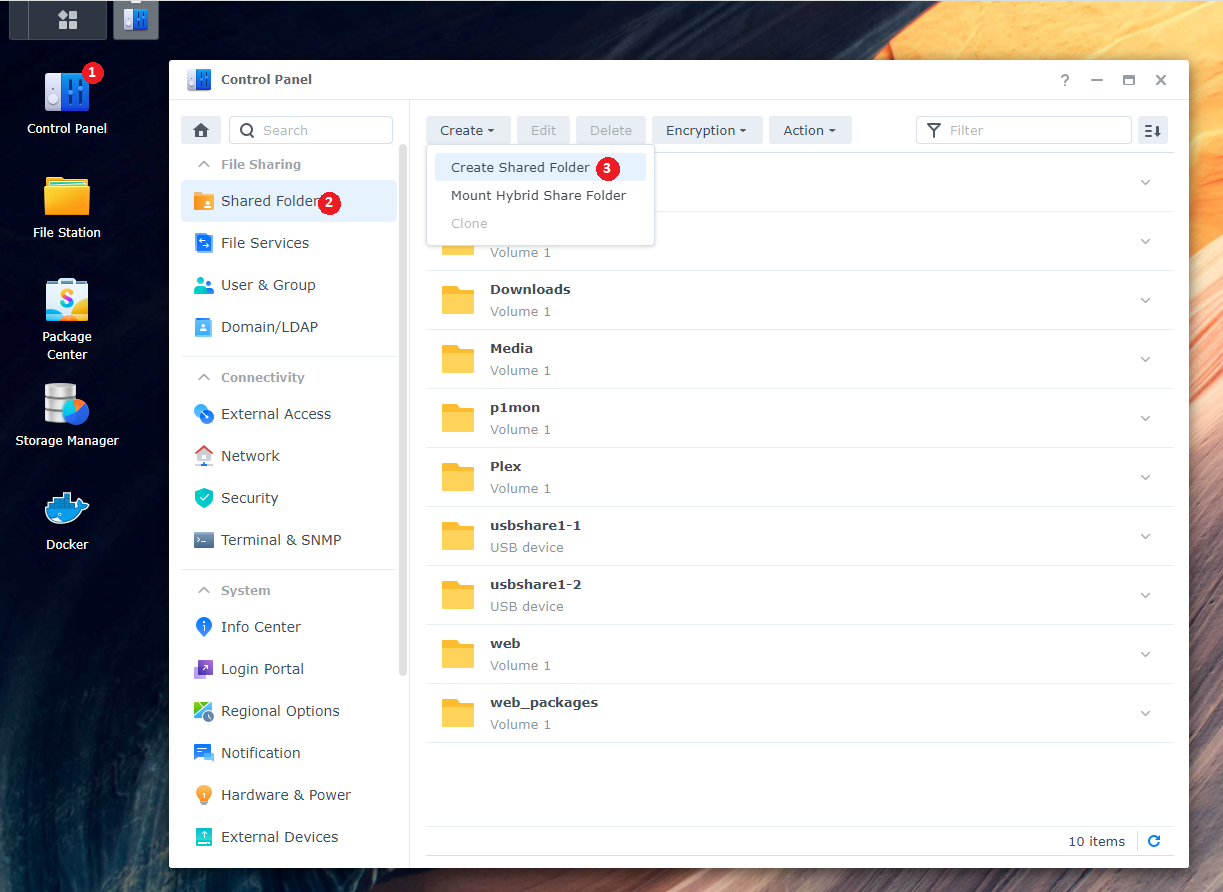
To create a new share:
Control Panel > Shared Folder > click Create > choose Create Shared Folder
Name this shared folder data. You can disable the trash can, up to you. Click next until you are done.
Create a user
We are going to create a new user that only has access to the share(s) that we use for the containers to run. You should not have the containers run as an admin/root user.
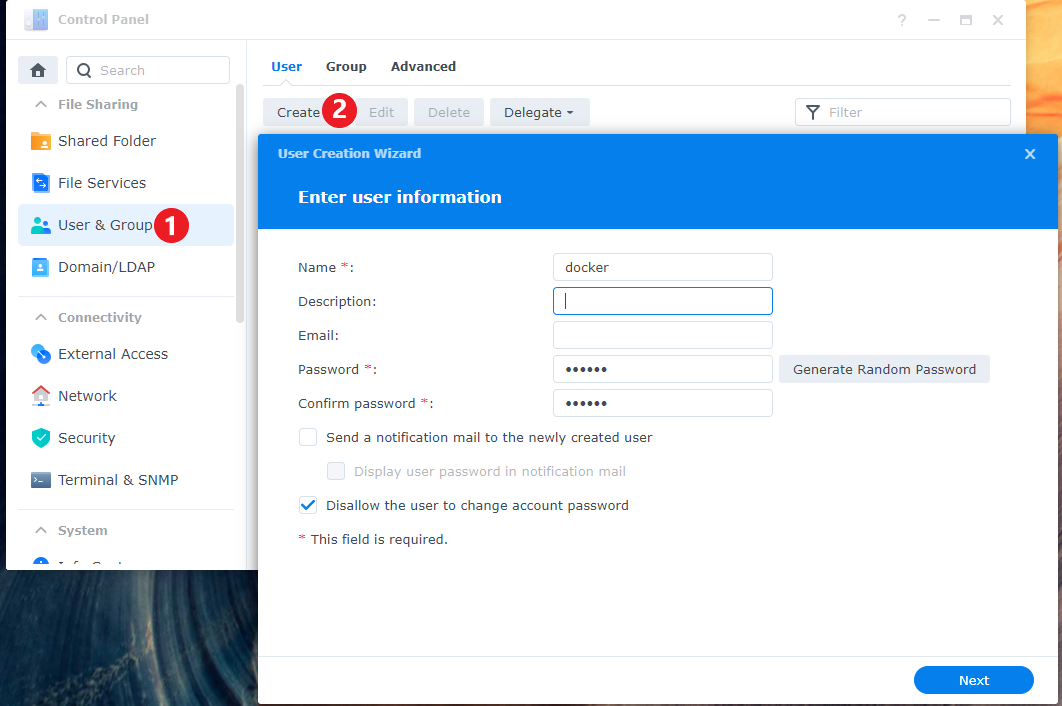
Go to Control Panel > User & Group
In the User section, create a new user. Name it whatever you like, but for this guide, we will use the name docker.
Fill out the rest of the information, generate a password or type your own.
Click next, you will now be able to select which group this user will belong to, it should only be the group users. Click Next.
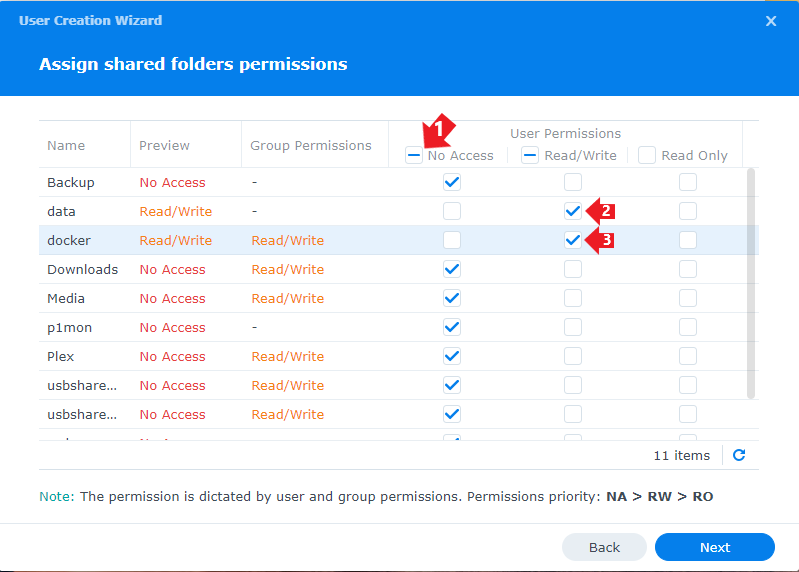
Assign shared folder permissions
In the next screen, you will be able to select which Shares this user will have access to, click No Access on the top, this will deny all access.
Now only select Read/Write on the shares docker and data (the share we created earlier).
Click Next until you reach Assign application permissions
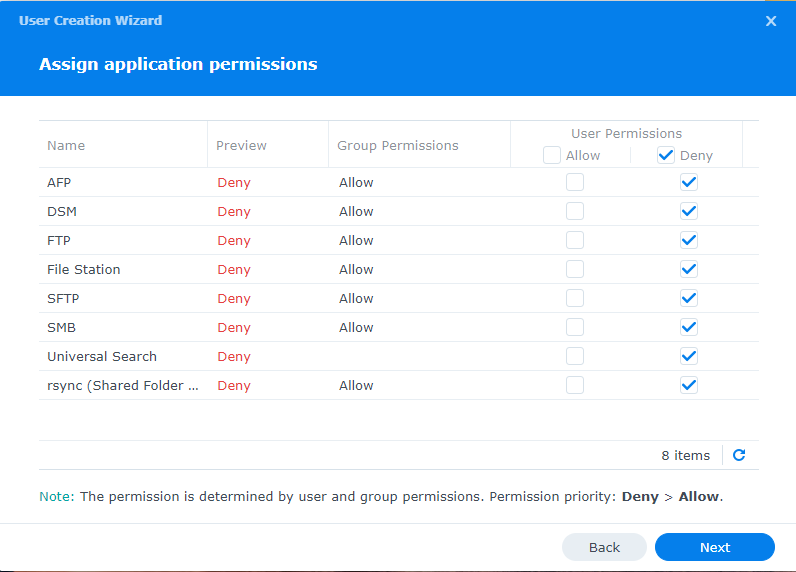
Assign application permissions
In this screen, you will be able to select which application this user will have access to. Check Deny for all applications.
Continue to click Next until you are finished.
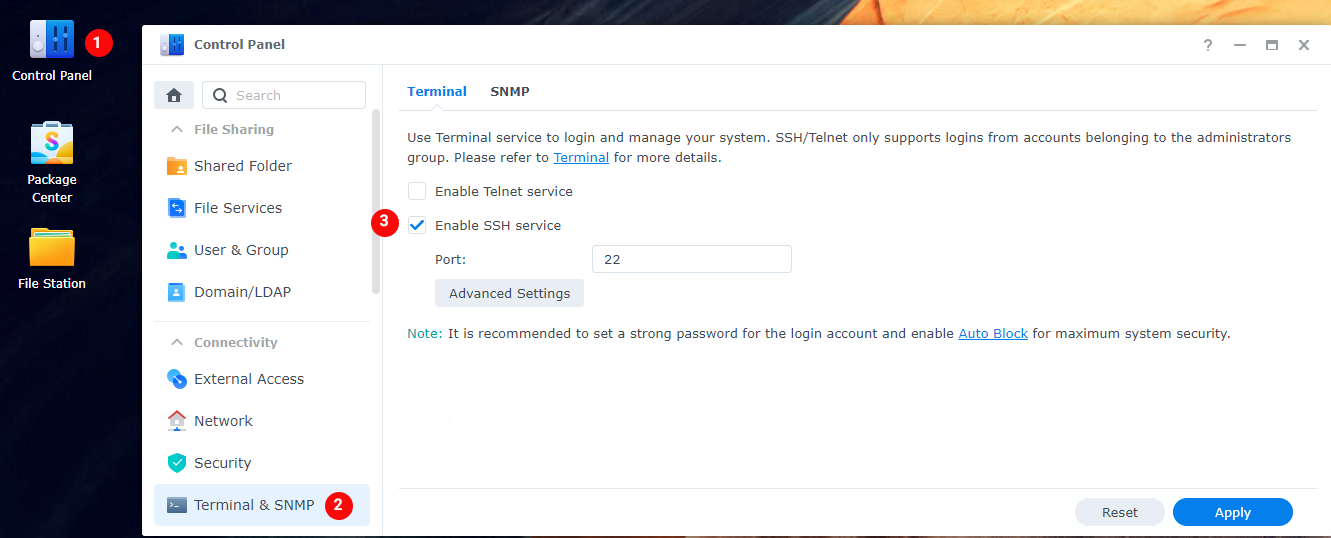
SSH
You are mostly going to use the terminal. Some parts will need the Synology web GUI. To enable terminal access, you need to enable SSH in the Synology Settings.
Control Panel > Terminal & SNMP > Enable SSH service
Then use a program like Putty{:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"} or Powershell/Terminal to SSH into your Synology.
Enter the login information of a Synology user account that has admin privileges, as only members of the 'administrators' user group can use SSH.
If you get a message asking if you want to trust the key, just press OK or ACCEPT.
PUID and PGID
For the Docker container to access the shares on Synology, we need to know the user ID (PUID) and group ID (PGID) from the docker user we just created.
Once logged in to the terminal type id docker. If you used a different username, change docker to the one you used.
This will show you the UID (aka PUID).
In the screenshot above this is 1035 for the docker user and 100 is the GID (aka PGID) for the user's group.
Save these values for later use.
Create Folder Structure
Let's create a good folder structure on the shares we use (docker and data). This will be done with a few commands.
The structure will look like this. You can of course edit this, but do this when you know what you are doing. We are using lowercase on all folders on purpose, being Linux is case-sensitive.
{! include-markdown "../../../includes/hardlinks/docker-tree-full.md" !}
{! include-markdown "../../../includes/hardlinks/bad-path-suggestion.md" !}
To create the folder structure for your media library and also for your preferred download client, run one or both of the following commands:
If you use usenet
mkdir -p /volume1/data/{usenet/{incomplete,complete}/{tv,movies,music},media/{tv,movies,music}}
If you use torrents
mkdir -p /volume1/data/{torrents/{tv,movies,music},media/{tv,movies,music}}
Appdata
Your application data will be stored in the docker share in the folder called appdata (/volume1/docker/appdata)
Create these folders with the command below, or create them in File Station manually.
mkdir -p /volume1/docker/appdata/{radarr,sonarr,bazarr,plex,prowlarr,pullio}
You can add your own subfolders for your download client(s) using the command above, by adding the name to the command.
So your appdata folder will look like this.
docker
└── appdata
├── radarr
├── sonarr
├── bazarr
├── plex
├── prowlarr
├── pullio
├── (your download client, i.e. nzbget; sabnzbd; qbittorrent)
└── (other applications)
Needed files
Now we are ready to move to the installation of containers.
For this, we need two files:
docker-compose.yml.env
We will start by downloading the docker-compose.yml file
Download this docker-compose.yml{:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"} to your /volume1/docker/appdata location so you can get your important stuff together. Or use the command below:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TRaSH-/Guides-Synology-Templates/main/docker-compose/docker-compose.yml -P /volume1/docker/appdata/
What's included in the compose and what is not included
This docker-compose file will have the following docker containers included.
- Radarr
- Sonarr
- Bazarr (Subtitle searcher and downloader)
- Plex
- Prowlarr (indexer/tracker manager)
What's not included (and where are the download clients?).
We didn't add a download client to it, because it depends on what you prefer (usenet/torrent) and which client you prefer. We have a repository Repository{:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"} on Github where we provide and maintain some templates that are ready to use with the main docker-compose.yml.
The only thing you need to do is copy & paste what's inside the template file into the main docker-compose.yml on the bottom, the templates also have a command that you need to use to create the appdata folder that we explained earlier. Without the appdata folder for the application, the creation of the container will fail because of the missing folder.
Second, we will download the .env file
Download this .env{:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"} to your /volume1/docker/appdata location next to the docker-compose.yml. Or use this command:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TRaSH-/Guides-Synology-Templates/main/docker-compose/.env -P /volume1/docker/appdata/
!!! warning
:bangbang: MAKE SURE THE FILE KEEPS THE ORIGINAL NAME `.env` WITH THE DOT BEFORE IT :bangbang:
Changes and preparations
!!! tip
If you need to edit docker-compose.yml or the .env file we advise to use [Notepad++](https://notepad-plus-plus.org/){:target="\_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"} or [Visual Studio Code](https://code.visualstudio.com/){:target="\_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"}
The .env file we downloaded holds the variables/information you need to change for everything to work. I added explanations in the .env file.
- DOCKERCONFDIR (only change this if you know what you're doing and decide to use another path than this guide used)
- DOCKERDATADIR (only change this if you know what you're doing and decide to use another path than this guide used)
- PUID/PGID (this info you got earlier from HERE)
- TZ (Change to your timezone, can be found HERE{:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"})
- Install and Create a task scheduler for Pullio, so your containers stay up to date.
!!! info ""
The `.env` holds more variables/information for other containers you don't need to remove those variables and will be only used when you install the other containers.
Pullio - Auto update docker-compose the correct way
Pullio allows you to automatically update your containers. And send you a notification through various means. We use a Discord Webhook.
First, you need to download Pullio
sudo curl -fsSL "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hotio/pullio/master/pullio.sh" -o /usr/local/bin/pullio
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/pullio
For Pullio to do its job, you will need to create a Scheduled Task in your Task Scheduler that runs for example at 4AM with root privileges.
Control Panel > Task Scheduler > click Create > choose Scheduled task - user-defined script
Give the task a name so you know what it does. Choose user root.
In the Schedule tab choose when and how often you want it to check for updates.
At Task Settings tab, add the following line in the Run Command section:
/usr/local/bin/pullio > /volume1/docker/appdata/pullio/pullio.log 2>&1
It can be frustrating to test the script if no docker image updates are available, therefore you can run the command sudo pullio --debug` and the script will behave as if an update is available. If you have set to receive notifications, you should receive them.
More info about Pullio HERE{:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"}
Permissions
Now we need to make sure that the newly created files and folders have the correct permissions.
If you have an existing library, it is advised to move these to the new data share prior to running the commands below.
!!! note
If you're using a different user than `docker` (the user-generated in the beginning), then you need to change the `docker:users` part in the command below!!!
sudo chown -R docker:users /volume1/data /volume1/docker
sudo chmod -R a=,a+rX,u+w,g+w /volume1/data /volume1/docker
!!! note
If you move files from a different library into the newly created library afterward, you need to rerun these commands. !!!
Run the Docker Compose
!!! tip
make sure you delete/remove all your existing dockers from the Docker GUI and also remove your native installs (in Package Center) of these applications !!!
If you had previously installed apps, make a backup of their config folders or backup through the WebUI of the app.
If you have followed all the steps and your compose file is ready, run the following commands:
cd /volume1/docker/appdata
sudo docker-compose up -d
You will notice that all the images will be downloaded, and after that, the containers will be started. If you get an error then read what the error says and try to fix it (missing folders, permissions errors, etc). If you can't figure out the solution to your errors, join the guides-discord here{:target="_blank" rel="noopener noreferrer"} and create a support ticket.
If you need help setting up the applications, look at the Examples of how to set up the paths inside your applications.
!!! warning
If you need to make any changes, only edit the `docker-compose.yml` file. To activate the changes, [run the commands from here](#run-the-docker-compose) again.
Any changes you do/did in the GUI will be reverted when you run the docker-compose command.
Just don't use the GUI, only for information purposes !!!
{! include-markdown "../../../includes/hardlinks/docker-compose-commands.md" !}
--8<-- "includes/support.md"
Additional Synology Info
DSM Task for correctly reporting IP in Plex/Nginx/Etc
Due to some iptables configuration in DSM, you can get an incorrect IP reported in Plex or other apps that need an read/report the IP. To fix this, you need to add two rules to your iptables. unfortunately, those rules can sometimes be deleted at reboot or after DSM update.
To fix this, you will need to add a Scheduled Task that executes at boot as the root user which will check if the rules exist, and, if not - re-add them.
??? question "Task bash command - [Click to show/hide]"
```bash
--8<-- "includes/hardlinks/docker-iptables-fix.sh"
```